Business performance management (BPM) describes the approach that an organisation takes to guide its operation towards established goals.
This is achieved by translating organisational goals, via a strategy, into performance measures - otherwise known as KPIs. Once these measures are established, we review performance against them and take corrective or reinforcing action to drive the organisation forwards.
History of BPM
- Late 1400s: Luca Pacioli describes double-entry bookkeeping and urges business owners to arrange their affairs systematically.
- Late 1700s: Cost accounting develops as the industrial revolution leads to businesses growing larger. Wedgewood formalises the structure of his pottery business with specialised labour shops, managers and foremen. Cost accounting begins to take shape.
- 1819: The Springfield Armory implements mass production. A formal business structure -- cost accounting for payroll, time and materials, and defined management practices -- is introduced to support this.
- 1853: The first professional bodies for accountants in the world are formed: The Institute of Accountants in Edinburgh, and the Institute of Accountants in Glasgow.
- 1911: Frederick Winslow Taylor publishes The Principles of Scientific Management. His ideas revolutionised BPM, but nowadays seem excessively harsh.
- 1920s: The Du Pont Company develops the concept of return on investment, which leads to a series of financial metrics. Financial metrics are adopted by General Motors, creating a results-based approach. Henry Ford takes a process-based approach. These views still compete in today's business climate.
- 1960s: Models of BPM mushroom. Theorists develop management by objectives, the performance pyramid, the balanced scorecard, lean, benefits realisation and many others.
Despite the rush of development in the last century, BPM is essentially an idea from the fifteenth century!
What can I do with it?
Humans are goal-seeking animals -- there is always a goal, a deadline, a target or a budget to meet. We plan and organise our efforts in the light of the objectives we have -- pretty much everything we do is target-focused.
This diagram illustrates the notion of business performance management:
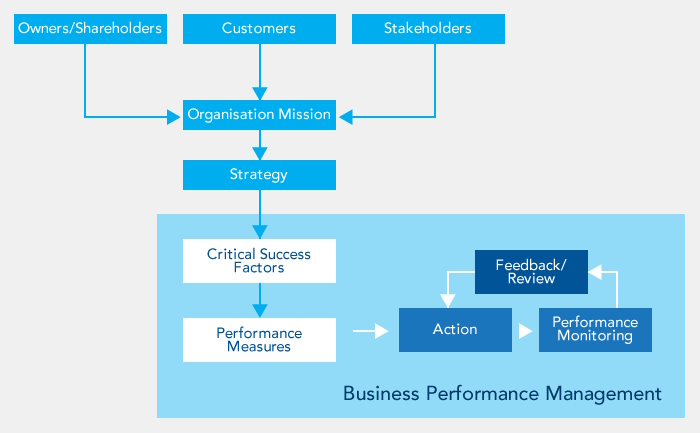
The role of management is to work to ensure the organisation achieves its purpose, and to marshal the efforts of everyone in the organisation behind this purpose. Business performance management is the structure for measurement, feedback and corrective action that is put in place so that managers can monitor the implementation of the organisational strategy.
Check our Ross' 4-hour course on BPM, which is verifiable CPD for accountants, here!

You need to sign in or register before you can add a contribution.